LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting has revolutionized the way we illuminate spaces, offering high energy efficiency, long lifespan, and superior brightness compared to traditional light sources. However, despite their many benefits, LEDs have a significant thermal management challenge that needs to be addressed to ensure performance and longevity. In particular, managing the heat generated by LEDs through effective thermal design is crucial, with heat sinks playing a pivotal role in this process.
LEDs are solid-state light sources, meaning they produce light through an electrical current passing through a semiconductor material. While LEDs are more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, they are still not perfect in terms of energy conversion. Only about 15% to 35% of the electrical energy is converted into visible light; the rest is converted into heat.
When multiple LED chips are densely packed into a single lighting device, which is often the case to achieve sufficient brightness, the heat generation increases significantly. If this heat is not efficiently dissipated, it can cause several problems, including:
Increased Junction Temperature : The junction temperature of the LED chip rises as heat accumulates. Higher junction temperatures reduce the efficiency of light production, leading to a lower light output.
Degradation of Light Quality : Heat affects the color consistency and quality of light emitted by the LED. A rise in temperature can cause shifts in color temperature, impacting the overall lighting performance.
Accelerated Aging : Continuous exposure to high temperatures accelerates the aging of LED chips. This shortens the overall lifespan of the lighting fixture and reduces reliability.
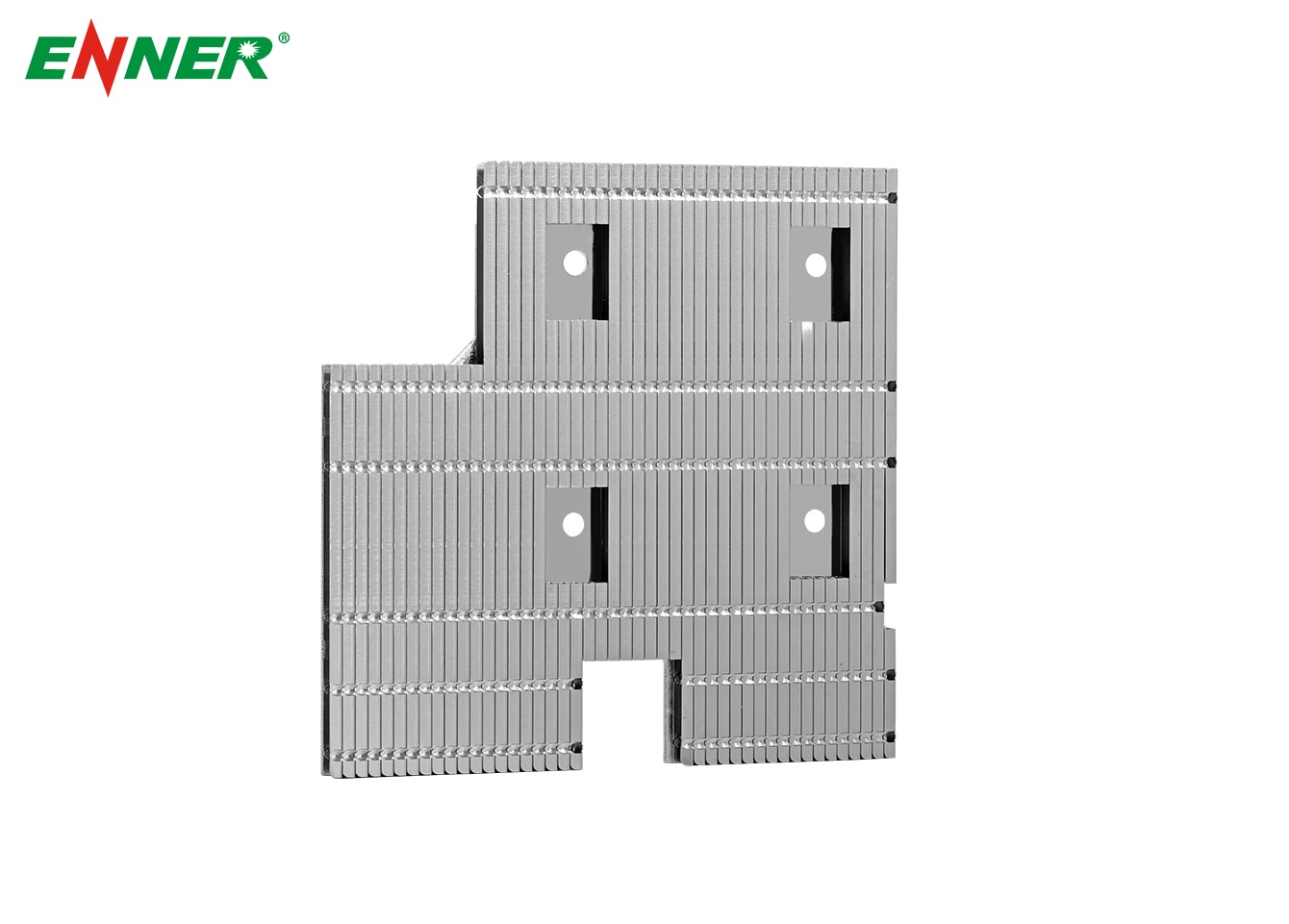
The primary challenge in LED lighting design is how to manage and dissipate the heat generated by the densely packed chips. Heat sinks play a crucial role in solving this issue by providing an efficient way to transfer heat away from the LED source.
Heat Conduction : In LED lighting, 75% of the generated heat is transferred via conduction. The heat is conducted from the LED chip to the LED base (substrate) and then to the heat sink. The heat sink, made from high-thermal-conductivity materials such as aluminum or copper, acts as a conduit to channel heat away from the chip.
Heat Convection : Once the heat is transferred to the heat sink, it is dissipated into the surrounding environment through convection. In this process, air flows over the surface of the heat sink, carrying away the heat and preventing it from accumulating around the LED.
Minimizing Junction Temperature : By effectively transferring and dissipating heat, the heat sink keeps the junction temperature of the LED chip low. This ensures that the LED operates within its optimal temperature range, preventing the aforementioned issues like reduced light output and accelerated aging.
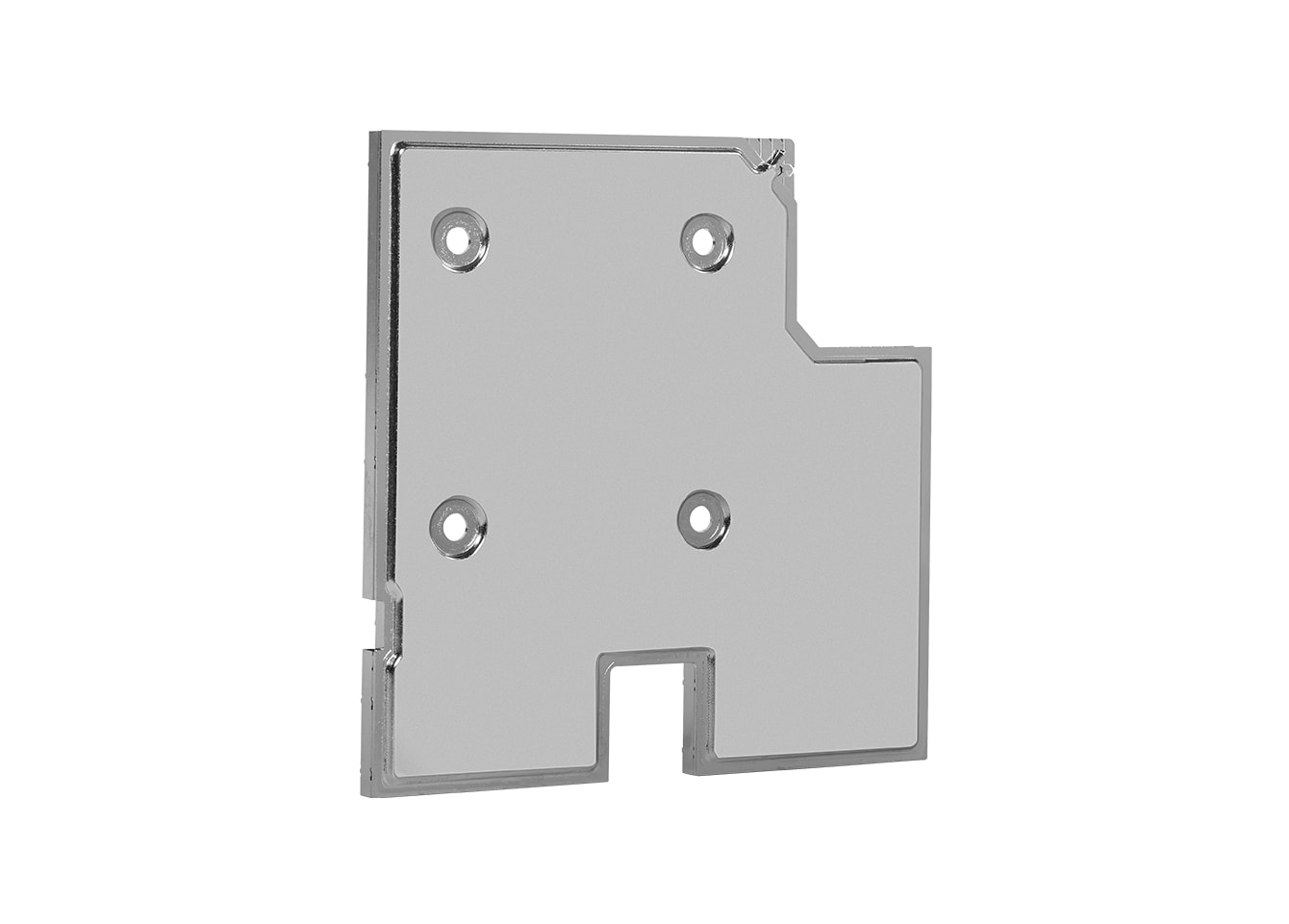
When designing a heat sink for LED applications, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal thermal performance:
Material Selection : Heat sinks are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity. Aluminum is the most commonly used material due to its excellent balance between thermal performance, weight, and cost. Copper is another option for higher-performance applications, though it is heavier and more expensive.
Surface Area and Fin Design : The design of the heat sink, particularly the surface area and fins, plays a critical role in how efficiently it can dissipate heat. Fins increase the surface area of the heat sink, allowing more air to flow over it and improving heat dissipation through convection.
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) : The interface between the LED chip, substrate, and heat sink should have minimal thermal resistance to ensure efficient heat transfer. High-quality thermal pastes or pads can be used to enhance the thermal conductivity between these components.
Airflow : Heat sinks rely on airflow to carry heat away from the surface. Passive cooling designs use natural convection, but in more demanding applications, active cooling solutions like fans can be integrated to enhance airflow and improve heat dissipation.
The thermal performance of LED lighting systems is directly tied to their ability to manage and dissipate heat effectively. As LED chips generate significant heat during operation, particularly when multiple chips are used in a single fixture, it is essential to ensure that this heat is properly managed to maintain optimal performance, light quality, and lifespan. Heat sinks play a vital role in this thermal management process by efficiently transferring and dissipating heat away from the LED source.
At ENNER , we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance heat sinks that meet the thermal demands of modern LED lighting systems. Our solutions ensure that your LED fixtures remain cool, efficient, and reliable, delivering the best performance in any application. With years of expertise in thermal management, ENNER is your trusted partner for advanced heat dissipation solutions.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.