In the realm of thermal management, particularly in high-performance electronics, maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial for ensuring reliability and efficiency. One of the most effective solutions for managing heat in such systems is the heat pipe heat sink. This article delves into what a heat pipe heat sink is, how it works, and where it is commonly used.
A heat pipe heat sink is an advanced thermal management device that leverages the principles of heat pipes and traditional heat sinks to dissipate heat from electronic components. It is designed to efficiently transfer and spread heat away from critical areas, ensuring that components such as CPUs, GPUs, and power electronics maintain safe operating temperatures.
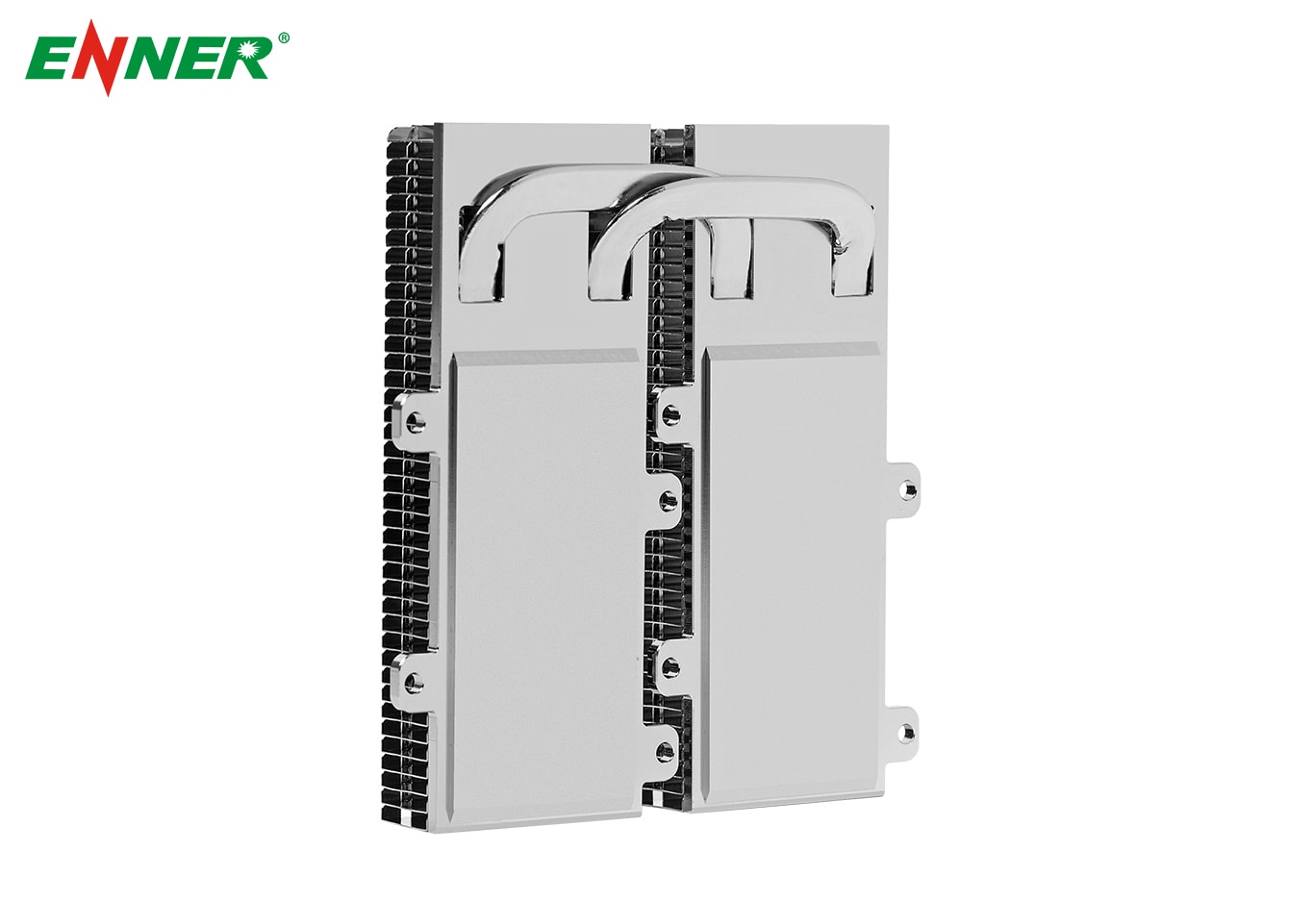

Heat Pipes : The core of the heat pipe heat sink, heat pipes are sealed tubes filled with a working fluid. The fluid absorbs heat at one end, evaporates, and then condenses at the cooler end, releasing the absorbed heat. This cycle repeats continuously, allowing for rapid heat transfer.
Fins : Fins are attached to the heat pipes to increase the surface area for heat dissipation. These fins are usually made of aluminum or copper and are designed to maximize airflow, enhancing the cooling process.
Base Plate : The base plate is in direct contact with the heat-generating component. It absorbs heat and transfers it to the heat pipes for further dissipation.
A typical heat pipe consists of a shell, a suction core and an end cap. The inside of the heat pipe is pumped into a negative pressure state and filled with a suitable liquid, which has a low boiling point and evaporates easily. The wall of the tube has an absorbent core, which is made of capillary porous material. One end of the heat pipe for the evaporation end, the other end for the condensation end, when the heat pipe end of the heat, the capillary tube in the liquid quickly evaporate, the vapor in the small pressure difference flows to the other end, and the release of heat, and re-condensation into a liquid, the liquid and then along the porous material by the action of the capillary force flows back to the evaporation section, and so on more than the cycle of the heat pipe from the end of the heat pipe to the other end. The cycle is rapid and the heat is continuously transferred.
High Efficiency : Heat pipe heat sinks are incredibly efficient at transferring heat over long distances compared to solid metal heat sinks.
Compact Design : Despite their efficiency, heat pipe heat sinks can be designed to be compact, making them ideal for applications with space constraints.
Passive Cooling : Since heat pipes do not require any moving parts, they provide passive cooling, which is silent and reliable over long periods.
Versatility : Heat pipe heat sinks can be used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems, due to their adaptability.
Computing Devices : In laptops, desktops, and servers, heat pipe heat sinks are commonly used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and other critical components.
Power Electronics : In power supplies and converters, heat pipe heat sinks manage the heat generated by high-power transistors and diodes.
LED Lighting : High-intensity LED lights use heat pipe heat sinks to dissipate heat and maintain the longevity of the LEDs.
Telecommunications : Base stations and other telecom equipment often rely on heat pipe heat sinks for effective thermal management in harsh environments.
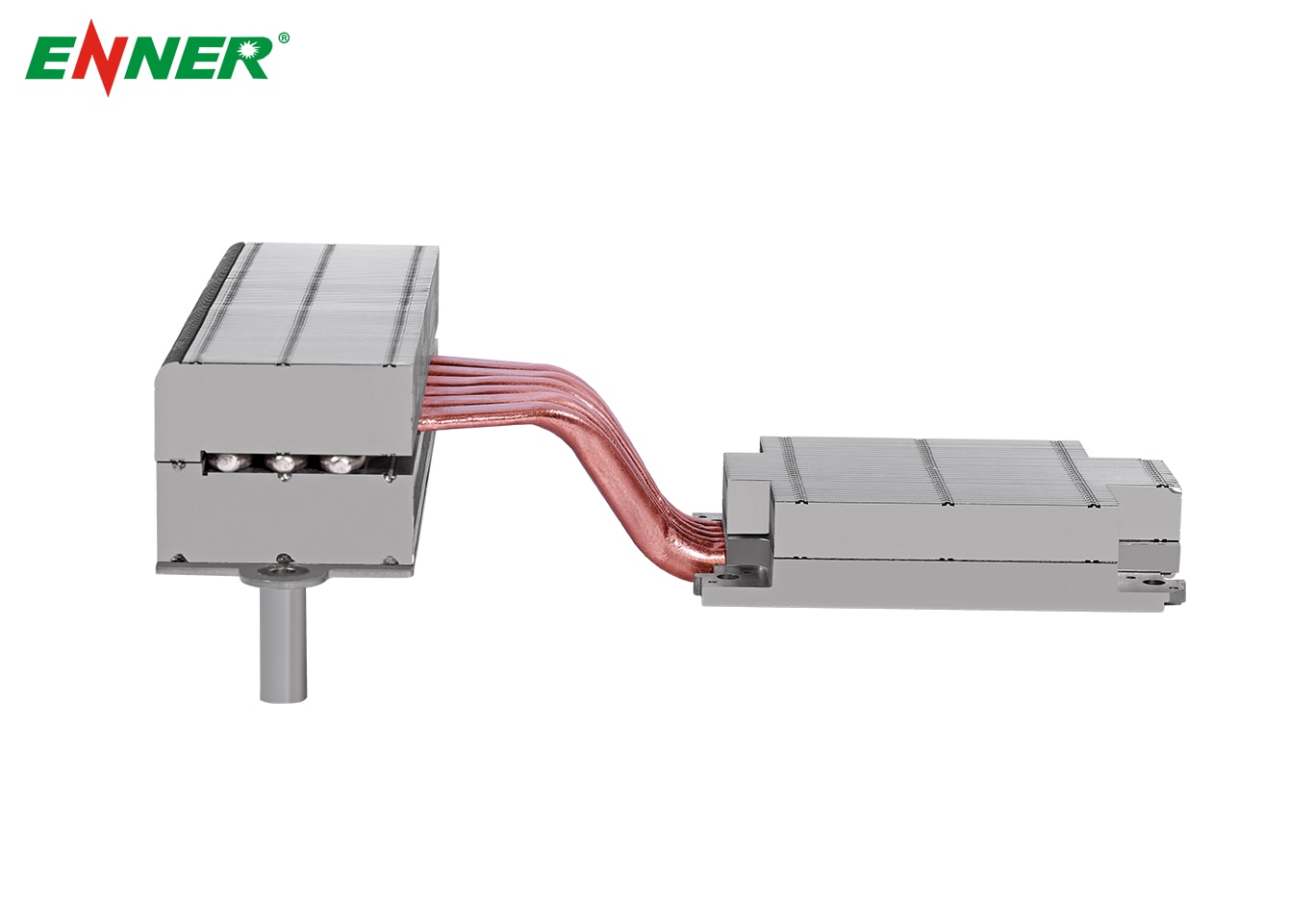
A heat pipe heat sink is an innovative and highly effective solution for managing heat in various high-performance applications. By combining the rapid heat transfer capabilities of heat pipes with the efficient dissipation provided by fins, these heat sinks ensure that electronic components operate within safe temperature limits, thereby enhancing performance and reliability. As electronics continue to evolve and become more powerful, the role of heat pipe heat sinks in thermal management will only grow in importance.
At Ennerhe, the research and development team consist of graduates from universities in the fields of thermodynamics, mold design and manufacturing, and materials science. With a complete heat dissipation simulation software and rapid samples production, the team can assist customers in designing the best solutions.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.