In recent years, the rapid advancement of electronic devices has transformed various industries, driving consumer demand for more powerful, compact, and efficient technology. This evolution includes a wide range of products, from smartphones and laptops to sophisticated microelectronics in industrial applications. However, as devices become smaller and more powerful, they generate significantly more heat, underscoring the urgent need for effective thermal management solutions. Among these solutions, heat sinks play a pivotal role in maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Heat is an unavoidable byproduct of electronic operations, primarily produced by high-performance processors, graphics units, and dense circuitry. As these components operate, they convert electrical energy into heat, which can accumulate if not properly dissipated. This heat buildup can lead to overheating, resulting in reduced efficiency, unexpected shutdowns, and even permanent damage to components. Effective thermal management, particularly through the use of heat sinks, is essential to maintain the integrity and longevity of electronic devices.
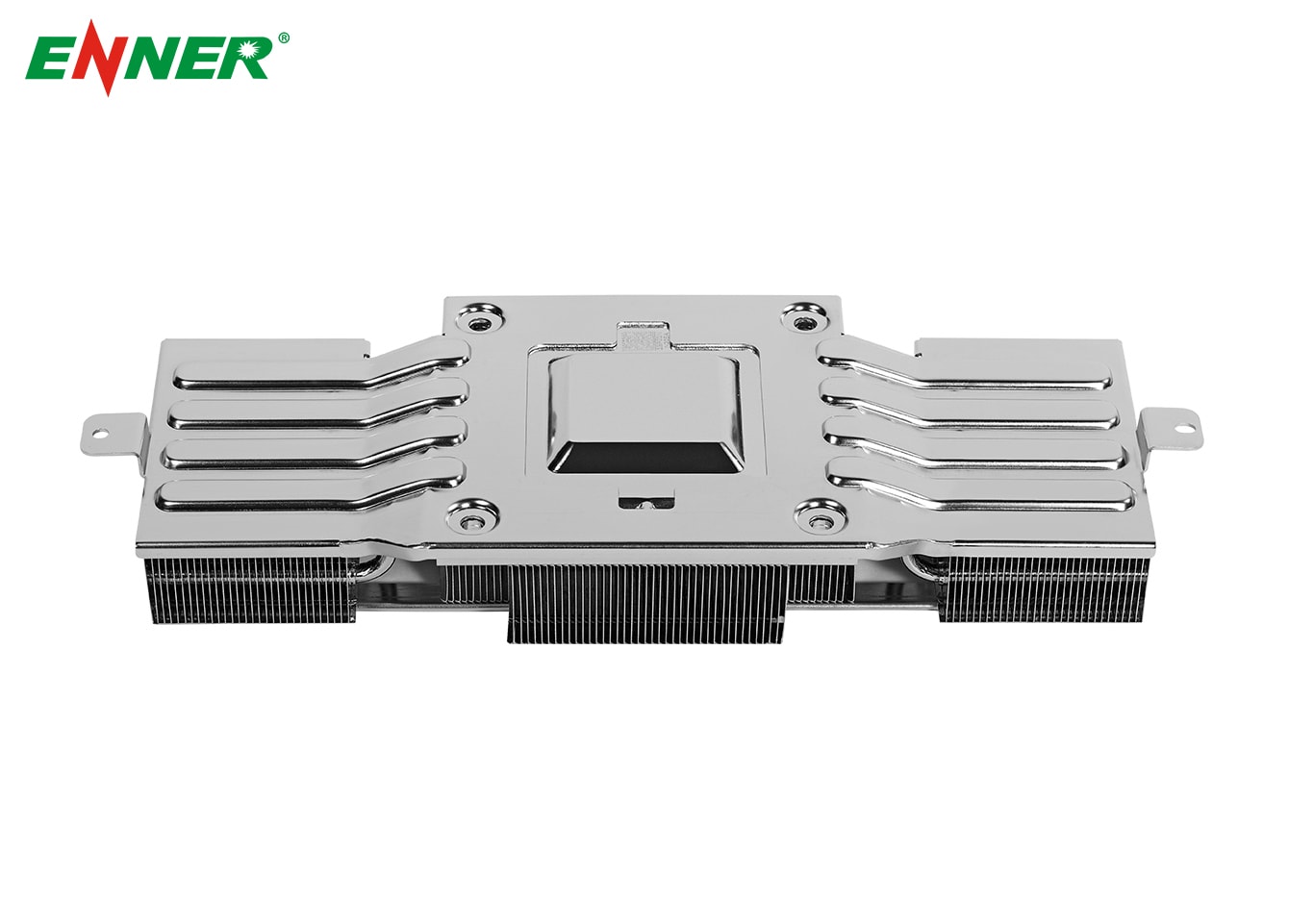

Heat sinks are specifically designed to dissipate heat from critical electronic components by maximizing the surface area available for heat transfer. They operate through two primary mechanisms: conduction and convection.
Effective heat sink design requires careful attention to several factors:
Heat sink designs can be categorized into several types, each tailored to specific cooling needs:
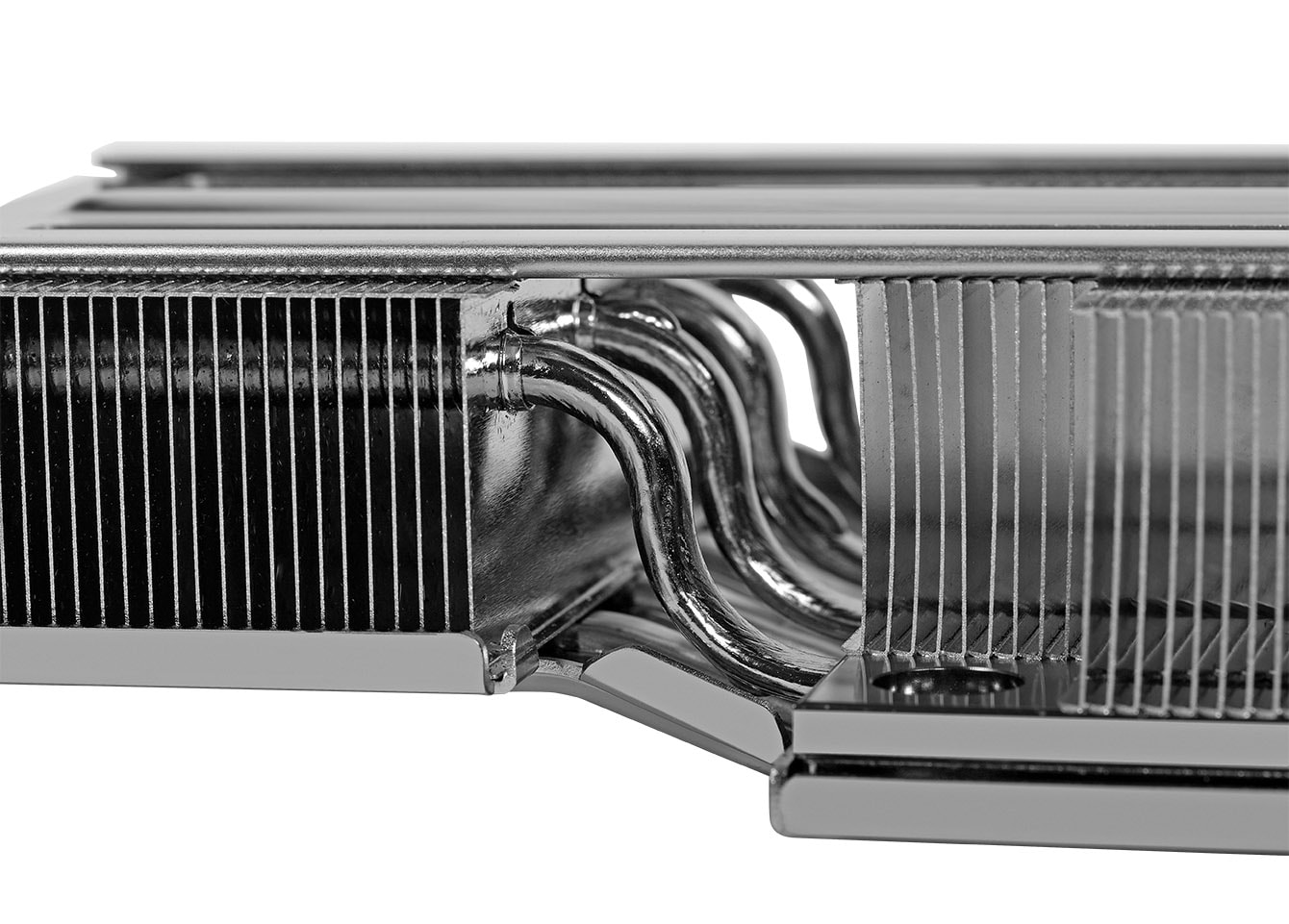
The choice of materials for heat sinks significantly affects their performance. Aluminum is favored for its balance of thermal conductivity, weight, and cost, while copper excels in thermal dissipation but may increase overall weight and expense. Emerging materials, such as CarbAl, which combines aluminum and carbon-based materials, show promise for future heat sink applications due to their high thermal conductivity.
Heat sinks are integral to the thermal management of electronic devices, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. As electronic components become more compact and powerful, the heat generated can significantly affect their functionality. Effective heat sinks dissipate this excess heat, preventing overheating and protecting sensitive components from damage.
As technology continues to advance, the need for innovative heat sink designs and materials becomes increasingly critical. We encourage readers to prioritize heat management strategies in their projects, recognizing the essential role of heat sinks in ensuring their electronic devices operate efficiently and reliably.
To learn more about advanced thermal management solutions and how heat sinks can enhance your applications, please visit ENNER's website. Explore our range of products and resources designed to help you achieve optimal thermal performance in your electronic systems.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.