Liquid-cooled heatsink, as the name suggests, are devices that dissipate heat from electronic equipment or mechanical systems by means of liquid conduction. Compared to traditional air-cooled heatsinks, liquid cooled heatsinks are able to carry away the heat generated by the equipment more efficiently, making them the preferred choice for applications that require higher cooling performance, such as high-performance computers, servers, data centers, electric vehicles, and industrial equipment.
The core principle of liquid cooling heatsink is to utilize the high thermal conductivity and fluidity of the liquid, and circulate the liquid through the closed pipeline to absorb and conduct the heat generated by the equipment. Its typical workflow is as follows:
Heat absorption by heat source: The water-cooling head of the liquid cooling cooling system is close to the heat source (e.g. CPU, GPU or other high heat components) and rapidly absorbs the heat through the heat transfer material.
Liquid heat transfer: After absorbing the heat, the coolant circulates in the closed pipeline through the pump to take the heat away from the heat source.
Heatsink heat dissipation: After the coolant reaches the heatsink, the heat is diffused into the air through the metal fins of the heatsink, and the liquid is cooled at the heatsink.
Liquid circulation: the cooled liquid then returns to the water-cooling head through the action of the pump to start a new round of heat absorption and transfer, forming a complete circulation system.
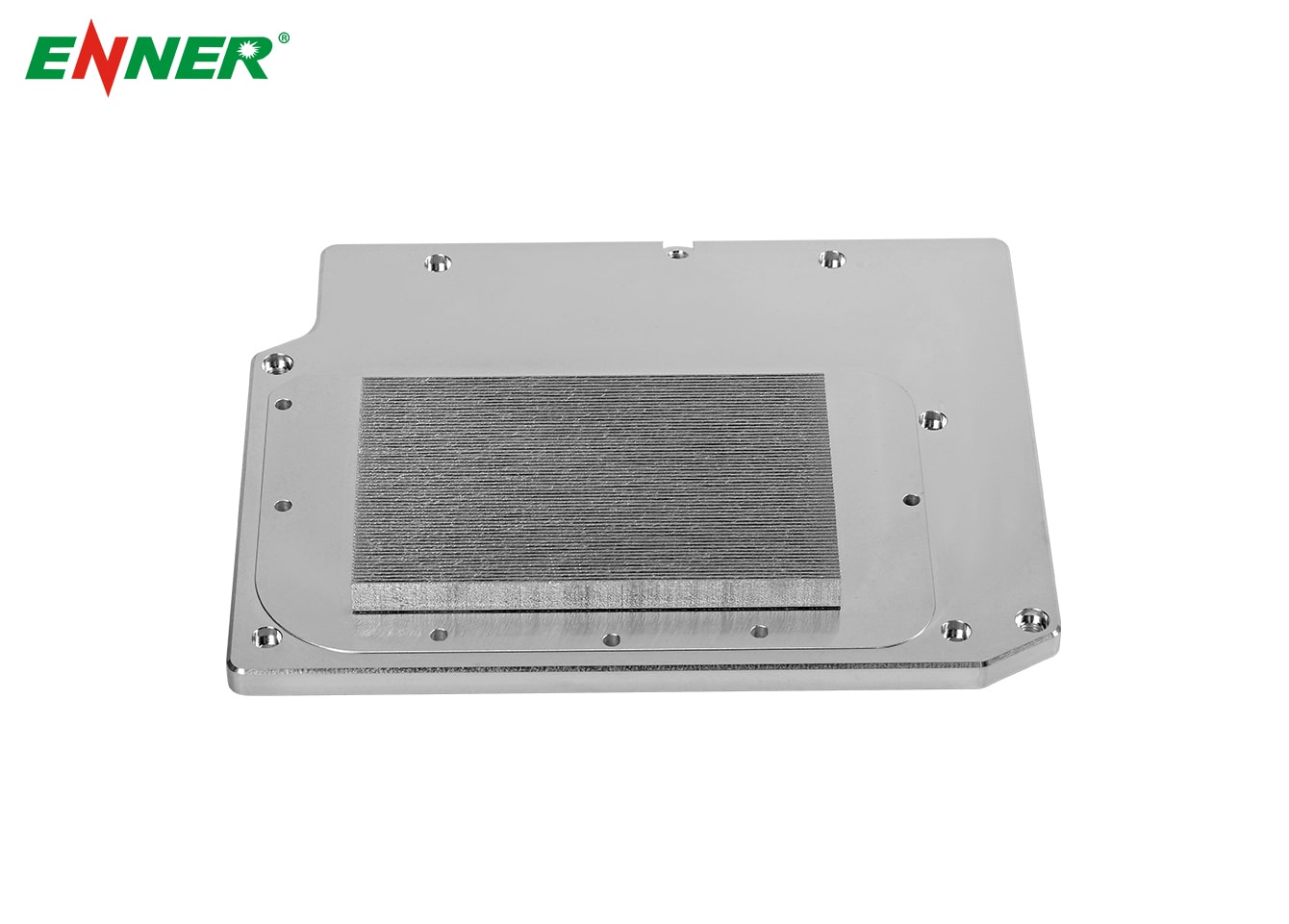

Better heat dissipation: Liquid has better thermal conductivity than air, so liquid cooling systems are able to conduct heat from the heat source to the heatsink more quickly and efficiently.
Quieter operation: Liquid-cooled systems typically rely on the circulation of liquid and operate with fewer fans, making them significantly quieter than traditional air-cooled cooling systems, especially in applications that require a low-noise environment.
Strong temperature control: Liquid-cooled systems can better control temperature fluctuations in equipment and maintain relatively stable operating temperatures, thus improving equipment performance and stability.
Suitable for high-performance equipment: For high-performance computer processors, graphics cards and other high heat-generating components, the cooling efficiency of the liquid cooling heatsink is much higher than that of the traditional air-cooled, which can ensure the stable operation of the equipment under high load.
Liquid cooling heatsink has a wide range of applications, covering a variety of industries and fields:
Computers and servers: In high-performance computers, workstations and data centers, liquid cooling systems can better handle the heat generated by high-power CPUs and GPUs, thus ensuring stable operation of the system under high loads.
Electric Vehicles: In electric vehicles, key components such as motors, battery packs and inverters generate a lot of heat during operation. Liquid-cooled heat sinks help these systems maintain stable operating temperatures through more efficient heat dissipation.
Industrial equipment: Many industrial equipment generates a large amount of heat during long-term operation, especially in the field of high-precision machining, liquid cooling heatsink ensures that the equipment can continue to maintain a highly efficient and stable state.
Despite the obvious advantages of liquid cooled heatsinks in terms of heat dissipation performance, there are some challenges and limitations:
Higher cost: Liquid-cooled systems are typically more complex than air-cooled systems and require more components such as pumps, coolant, piping, etc., making the initial installation cost relatively high.
Maintenance Requirements: Liquid-cooled systems require regular inspection and maintenance, including coolant replacement, leak prevention, etc. These maintenance requirements make liquid-cooled systems relatively expensive to install. These maintenance requirements make liquid cooling systems more complex than air-cooled systems.
Footprint: Liquid-cooled systems tend to be larger than conventional air-cooled systems and may not be suitable for certain space-constrained applications.
Liquid-cooled heatsinks are becoming an essential cooling solution in high-performance equipment due to their superior cooling efficiency, low noise levels and stable temperature control. Although the initial installation cost and maintenance complexity is relatively high, its performance and thermal efficiency over a long period of time makes it the preferred choice in many industries.
At ENNER , we offer a wide range of solutions to meet your thermal management and machining needs, including heatpipe cooling systems , vapor chamber heatsinks , extrusion heat sinks , skived heat sinks , zipper fin heat sinks , and stamped metal parts . Our expertise extends to providing CNC machining parts and accessories to ensure your projects are successful. Whether you’re building a CNC machine or looking for advanced cooling solutions, ENNER has the products and expertise to support your innovation.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.